Strategies for Intercropping in Sustainable Agricultural Growth
In the pursuit of sustainable agriculture, farmers around the world are turning to intercropping – a practice that involves growing multiple crops simultaneously in the same field. This approach offers numerous benefits, enhancing productivity, resource use efficiency, and resilience when implemented with care.
The comprehensive implementation guide provides practical steps for farmers to establish intercropping systems while minimising risks and maximising early benefits. Intercropping offers a proven pathway to resilient, productive agriculture in the face of mounting challenges from climate change, biodiversity loss, and food insecurity.
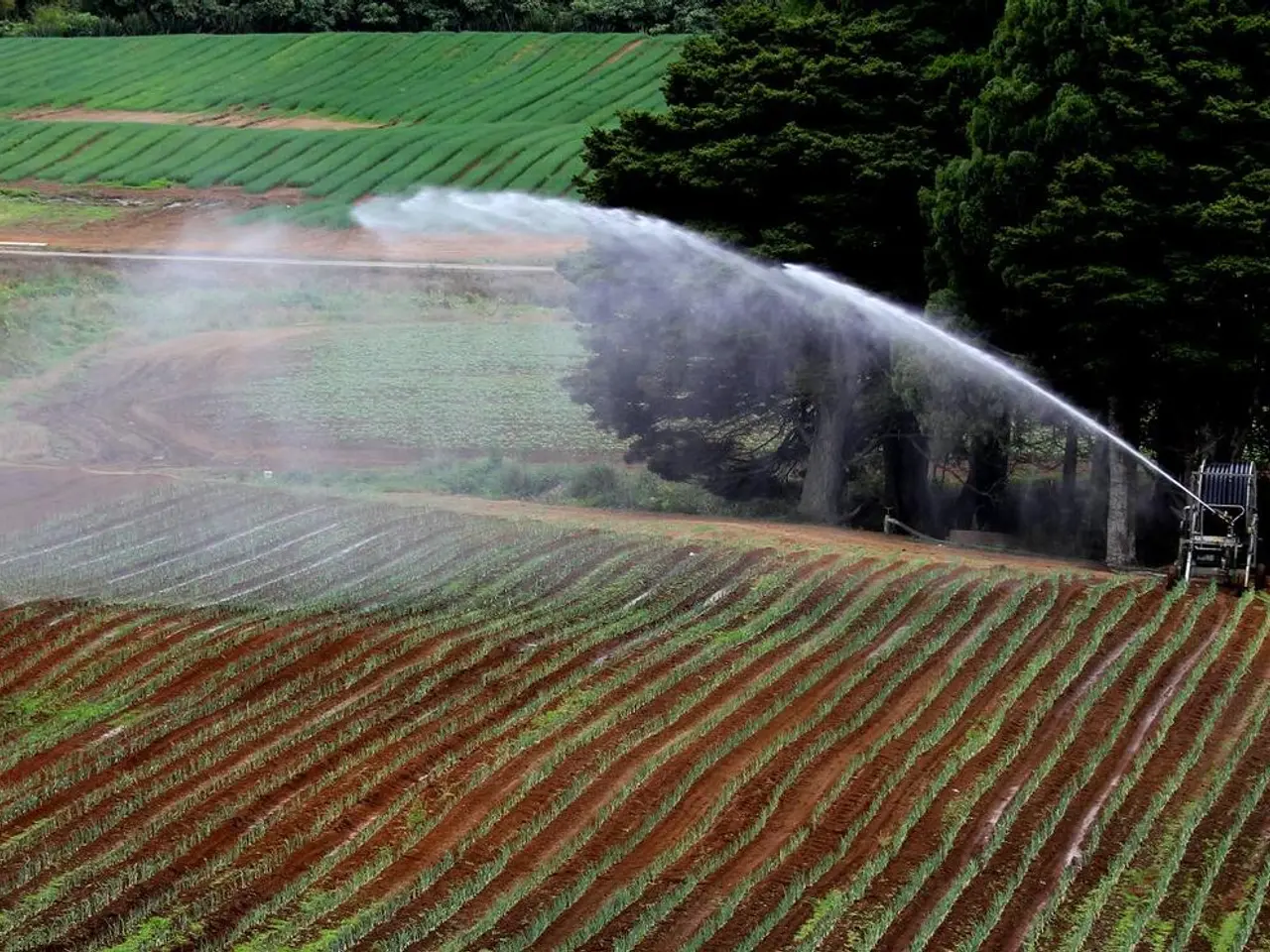
One of the primary advantages of intercropping is increased productivity and land-use efficiency. By growing two or more crops, such as sorghum and peanut, intercropping generally produces a greater total yield per area than growing each crop alone. Studies report over 90% of intercropping cases achieving a land equivalent ratio (LER) greater than 1, indicating efficiency gains.
Intercropping also provides risk mitigation. If one crop succumbs to pests, diseases, or unfavourable conditions, the other crop often remains unaffected or compensates, making farming outcomes more stable and reducing the risk of total crop failure.
Soil health is another key benefit of intercropping, especially when incorporating legumes. Intercropping enhances soil structure, increases microbial biodiversity, improves nutrient cycling, and boosts soil water retention, contributing to long-term sustainability and fertility maintenance.
Water use efficiency is another advantage of intercropping. By combining crops with different root depths or water needs, intercropping can reduce overall irrigation requirements by 15–20%, supporting water conservation in agriculture.
Diversified cropping also offers ecological benefits. Intercropping supports pest control, breaks pest and disease cycles, and fosters ecological balance. Intercropping systems support 34% more beneficial insects and 23% more bird species than monocultures.
Best practices for successful intercropping include choosing complementary crop pairs or groups, optimising fertilisation and water management, training and extension efforts, incorporating legumes carefully, and monitoring and adapting practices regionally.
For farmers, policymakers, and consumers committed to sustainable food production, intercropping provides a practical, profitable solution that benefits both people and the planet. The convergence of traditional knowledge with cutting-edge agricultural science promises to unlock even greater potential for intercropping in the decades ahead.
References:
[1] Greenland, D., et al. (2017). Intercropping for food security and sustainable agriculture. Journal of Sustainable Agriculture, 42(4), 371-387.
[2] Gomiero, A., et al. (2016). Intercropping: Challenges and opportunities for sustainable agriculture. Journal of Sustainable Agriculture, 39(4), 345-358.
[3] Fischer, J. (2011). Intercropping: The science and practice of mixed cropping. CABI.
[4] Nkoolu, M., et al. (2016). Intercropping and sustainable agriculture: A review. Journal of Sustainable Agriculture, 39(4), 339-344.
[5] Wani, S. P., & Khan, M. A. (2010). Intercropping: Strategies and benefits for sustainable agriculture. Journal of Sustainable Agriculture, 33(5), 447-460.
- Adopting plant-based intercropping systems, which involve growing different crops together, aligns with ethical and sustainable practices in agriculture, fostering resilience and productivity in the face of environmental challenges.
- In food-and-drink production, intercropping offers numerous benefits, such as enhanced land-use efficiency, water use efficiency, and soil health, providing a pathway toward sustainable agriculture and nutrition.
- By combining crops with diverse root depths and water needs, intercropping can reduce irrigation requirements by 15-20%, promoting sustainability and environmental-science in the food-and-drink industry.
- Intercropping systems foster higher biodiversity, supporting more beneficial insects and bird species than traditional monocultures, thus encouraging ecological balance and environmental conservation in the lifestyle and technology sectors.
- As we look toward the future, the integration of traditional farming wisdom with modern agricultural science offers exciting possibilities for intercropping's potential in delivering both economic and environmental benefits, contributing to a sustainable food-and-drink system for all.